Renewable Energy:
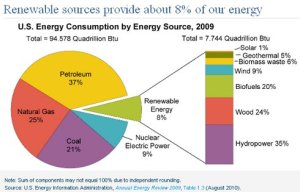
Renewable energy is energy that can be replaced naturally such as wind, hydroelectric, and solar power. The availability of these sources depends on the region. About 45% of energy in Sweden is renewable, about 16% in Germany and about 8% in the United States. Renewable energy is both affordable and efficient. Using these renewable sources can help reduce pollution and harmful emissions. Below is a breakdown of the sources of energy in the United States.
Solar energy is captured by the sun and stored in the solar panels or cells and then used for electricity. These devices work when photons strike and ionize the semiconductors on the panels which cause the atomic bonds to break. The electrons are then forced to flow in one direction creating an electric current. Solar panels have little to no maintenance cost and do not make any noise and are easy to install, making them easy to use at the residential scale along with industrial scale.
Hammarby Sjostad, Sweden is a city of innovation and multiple apartment complexes and buildings have solar cells or panels on the roofs to offset cost of electricity.
Another city where renewable energy is used heavily is Freiburg, Germany. There are houses specifically built with solar panels as the roof facing south into the sun in order to absorb as much sunlight as possible. Below is a picture of the houses.
Wind turbines have three wings similar to those of a plane and are attached to a stack ranges in height. When the air passes around the wing it causes the air pressure to be uneven because of the shape of the wing. Because the pressure is higher at one side of the wing, it causes the sing to spin. The blades are attached to a shaft which is attached to gears which are attached to a generator and then produces electricity. The taller the turbine is, the more electricity it can produce because there is more wind the higher the turbine is in the sky.
There are many advantages of wind turbines including being environmentally friendly because there is no use of fossil fuels used to generate the electricity. They take up less space so the surrounding area is still usable for other reasons such as agriculture. There are also many different sizes of wind turbines so there is a wind turbine that can fit into any type of area.
We visited a wind farm in Germany where the tower of the turbines were 150m tall and had 3 blades each at a length of 60m.
Hydroelectric plants are built on rivers that have a change in elevation. A dam is built and stores water in a reservoir. The water from the river turns the turbine propeller because of gravity and the turbine goes to the generator and produces power. The hydraulic turbine converts energy of the water into mechanical energy and the generator converts the mechanical energy into electricity.
There are not any poisonous bi-products or water or air pollution produced. The process is environmentally friendly and does not contribute to global warming. They do not contribute to the depletion of non-renewable resources. There is no need to import fuels to run the system, therefore, it is economical.
Conventional Energy:
Energy that cannot be replaced and is limited in quantity such as natural gas, nuclear, coal and oil. Nature is not able to keep up with demand because of the increased consumption rates of these sources.
There are advantages and disadvantages to using conventional and renewable energy. The use of renewable energy can help reduce the amount of harmful emissions produced and help the environment. Even though renewable energy is used less than conventional energy, it is on the rise and is continuing to increase.
References
- Cederquist, Bjorn. “Center for Environmental Information.” Sweden, Hammarby Sjostad. 12 May 2014. Lecture
- “Coal to Liquids.” Energy. American Geosciences Institute, n.d. Web.
- “Energy.” City of Las Vegas Solar Energy Portal/Ebergy. UNLV, n.d. Web
- “Energy 101: Wind Turbines”. US Department of Energy, 2014. Slide program.
- “Nuclear Power.” SPIEGEL ONLINE. N.p., n.d. Web.
- “Renewable Energy vs. Conventional Energy.” City of Las Vegas Solar Energy Portal | Renewable Energy vs. Conventional Energy. UNLV, n.d. Web.
- “Solar Energy.” Solar Energy. Solar Energy Industries Association. Web.
- “Wind Energy.” Wind Power. RenewableEnergyWorld.com. Web.








I found it very interesting the reactions Swedish people have to the idea of not using renewable energies since they are so used to it. The use of coal is very frowned upon and unheard of. One of the people we met on a tour, asked us if the United States was still relying on coal. We told him that we are almost entirely dependent on it still, which came as quite a shock to him. In Michigan, utilities are required to only have 10% renewables by 2015 which has not been easy to achieve due to industry unwillingess to change. Our current infrustructure is not designed for renewable energies although we have the feedstocks and technology to start building up our bioenergy and biomass industries when we decide to.